Schanz Pin Specification, Uses, Sizes and Surgical Techniques.

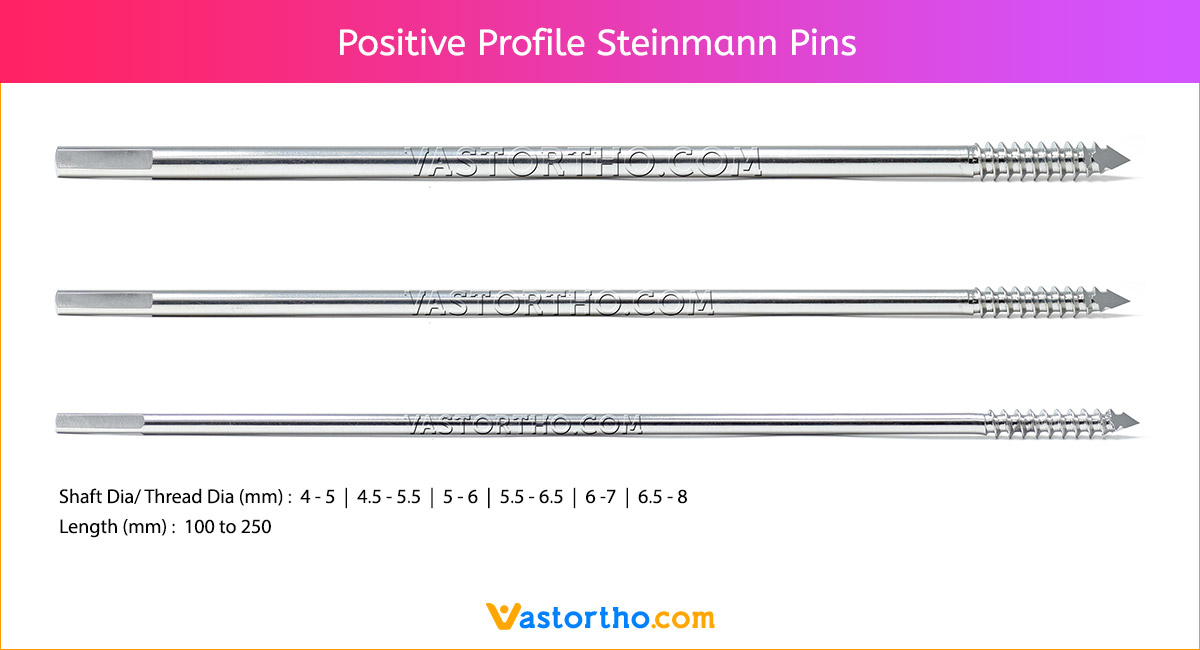
Schanz Pin is a metallic rod with pointed threads at one end and other end fashioned to fix into an attachment device.
Schanz Pins are available in various Types, lengths and diameters.
Types: Self Tapping, Self Drilling, Tapered Threaded
Diameters: 4mm, 4.5mm, 5mm, 5.5mm, 6mm, 6.5mm
Lengths: 60 mm to 300 mm
Schanz Pin Self Drilling has been specifically designed to optimise the bone/pin interface to reduce the occurrence of pin-tract related complications in external fixation.
The unique design of Schanz Pin Self Drilling reduces heat generation and insertion torque while improving pullout resistance in cortical and cancellous bone
Schanz Pin Self Tapping / Self Drilling Sizes
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4 x 20 x 80 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4 x 30 x 100 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4 x 40 x 125 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4 x 40 x 150 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4 x 40 x 175 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5 x 20 x 60 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5 x 20 x 80 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5 x 30 x 100 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5 x 40 x 125 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5 x 40 x 150 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5 x 40 x 175 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.0 x 30 x 100 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.0 x 40 x 125 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.0 x 60 x 150 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.0 x 60 x 175 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.0 x 80 x 200 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.0 x 80 x 250 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.5 x 30 x 100 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.5 x 40 x 125 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.5 x 60 x 150 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.5 x 60 x 175 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.5 x 80 x 200 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.5 x 80 x 250 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6 x 30 x 100 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6 x 40 x 125 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6 x 60 x 150 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6 x 60 x 175 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6 x 80 x 200 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6 x 80 x 250 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6.5 x 80 x 200 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6.5 x 80 x 225 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6.5 x 80 x 250 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6.5 x 90 x 275 mm
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6.5 x 100 x 300 mm
Schanz Pin Tapered Threaded Sizes
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5-3.5 x 20 x 80
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5-3.5 x 20 x 100
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5-3.5 x 30 x 100
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5-3.5 x 30 x 120
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5-3.5 x 30 x 140
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5-3.5 x 40 x 120
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5-3.5 x 40 x 140
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5-3.5 x 40 x 160
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 30 x 100
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 30 x 120
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 30 x 140
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 30 x 160
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 40 x 140
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 40 x 160
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 40 x 180
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 40 x 200
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 50 x 160
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 50 x 180
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 50 x 200
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 50 x 220
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 60 x 180
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 60 x 200
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 60 x 220
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 60 x 240
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 70 x 200
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 70 x 220
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 70 x 240
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 80 x 220
Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 80 x 250
Schanz Pin Indications for Use
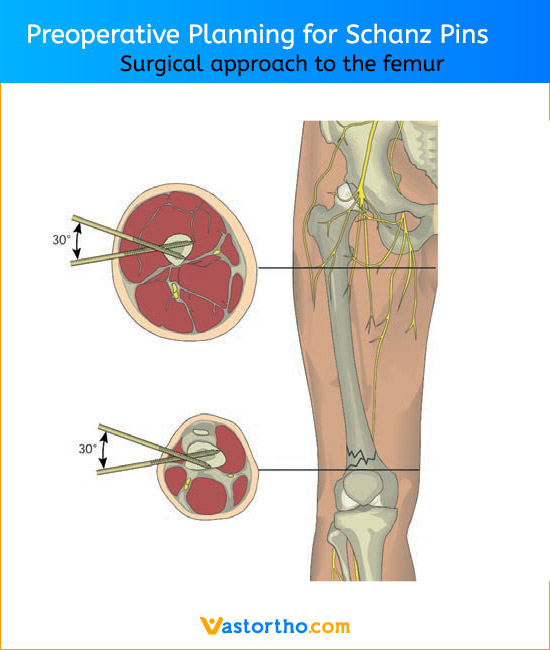
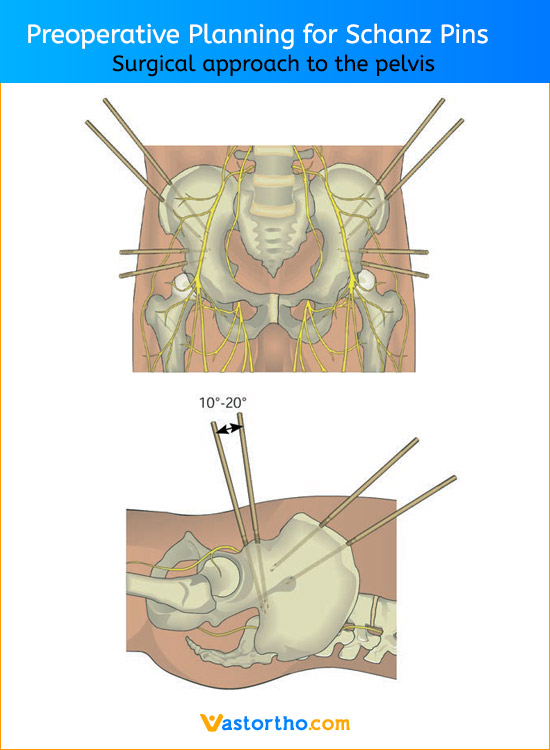
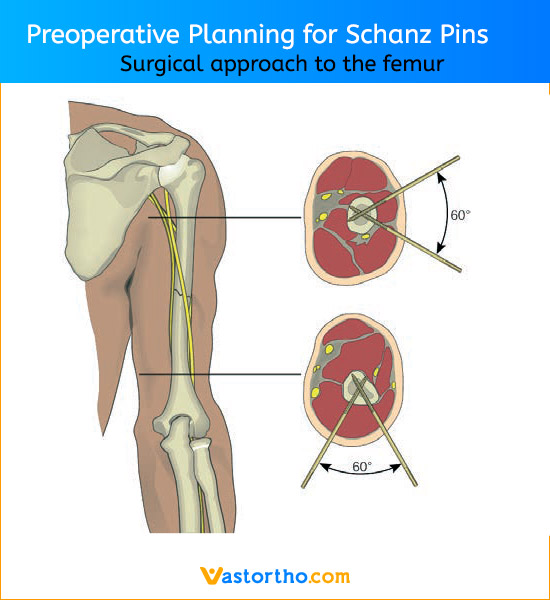
Schanz Pin is intended for use with an external fixation system for fracture fixation (open or closed); pseudoarthrosis or nonunion of long bones; limb lengthening by epiphyseal or metaphyseal distraction; correction of bony or soft tissue deformity; correction of segmental bony or soft tissue deformity; correction of segmental bony or soft tissue defects; and joint arthrodesis.
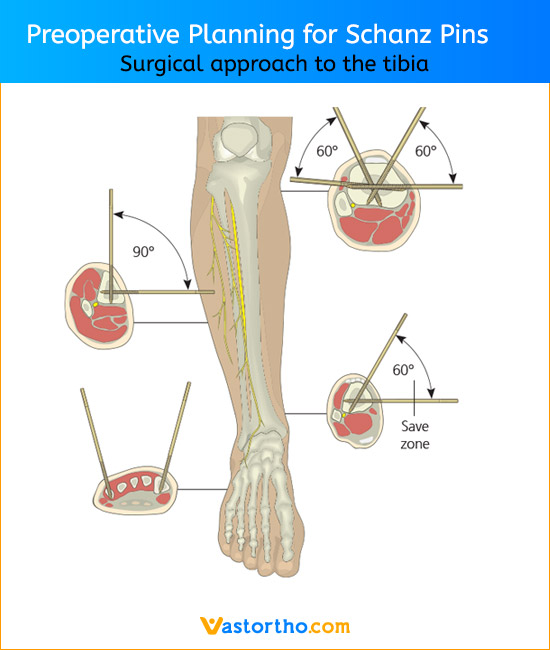
The chosen diameter of the Schanz Pin depends on the system that is selected for a particular fracture and on the bone size. For example, for a tibial fracture, Schanz Pin with a diameter of 5 mm are used (2.5 mm Kirschner wires or threaded pins are used for the small fixator).