Frame Plate Square Craniomaxillofacial Introduction, Features, Benefits, Indications, Precautions, Warnings and Surgical Technique.
The aim of surgical fracture treatment with Frame Plate Square Craniomaxillofacial is to reconstruct the bony anatomy and restore its function. According to the AO, internal fixation is distinguished by anatomical reduction, stable fixation, preservation of blood supply, and early, active mobilization.
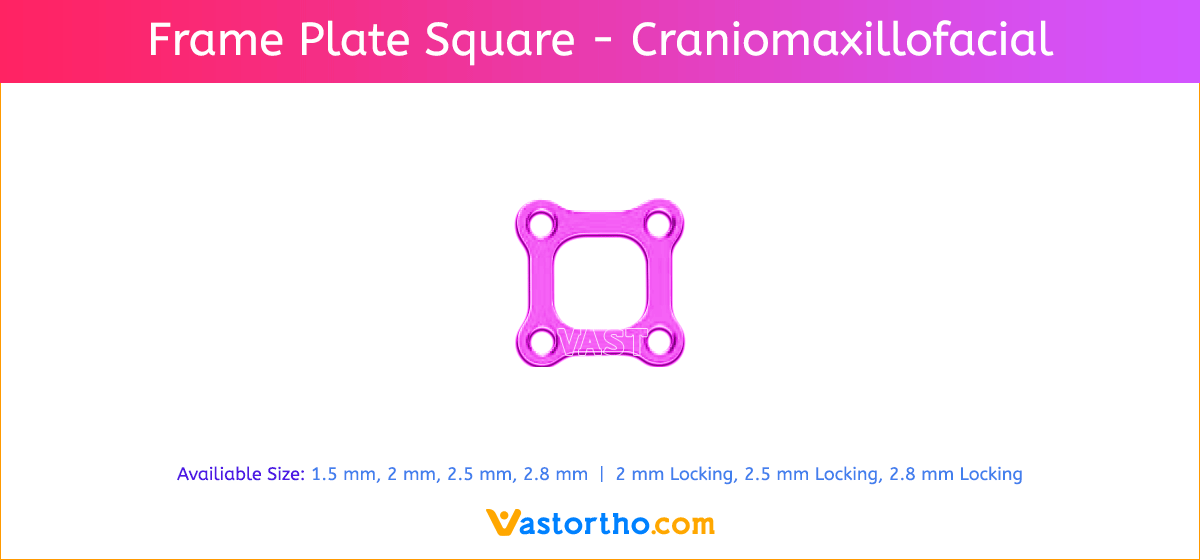
Frame Plate Square Craniomaxillofacial Features and Benefits
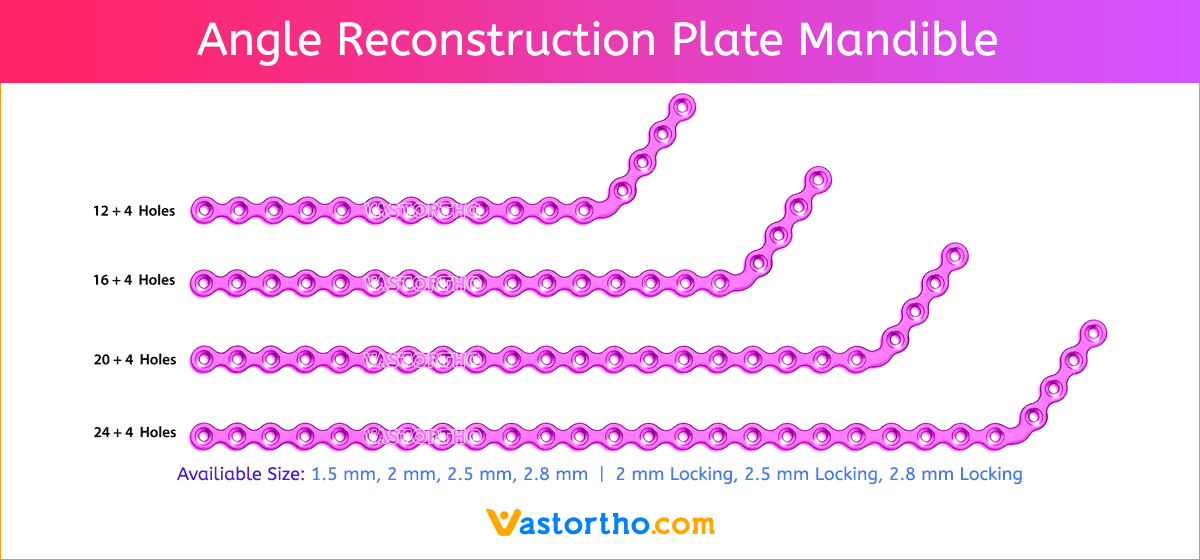
- Wide offering of Frame Plate Square geometries, sizes, and strengths
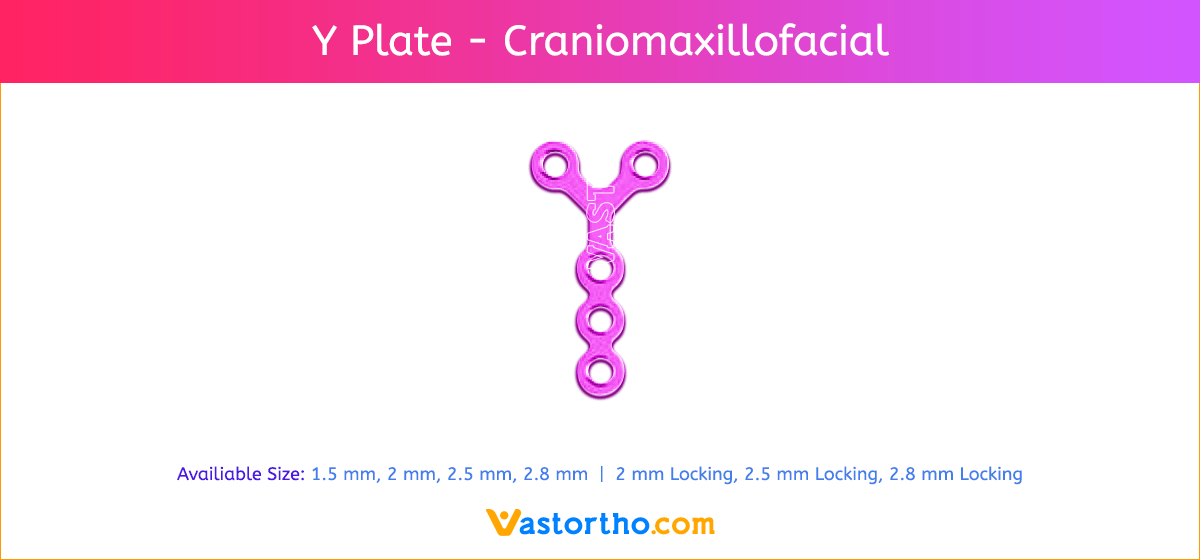
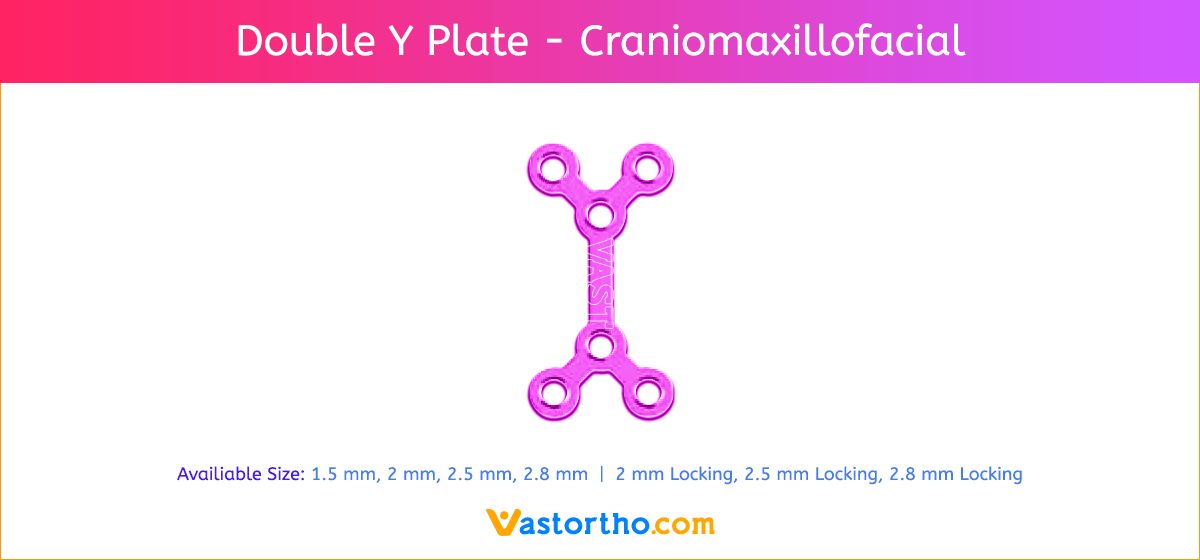
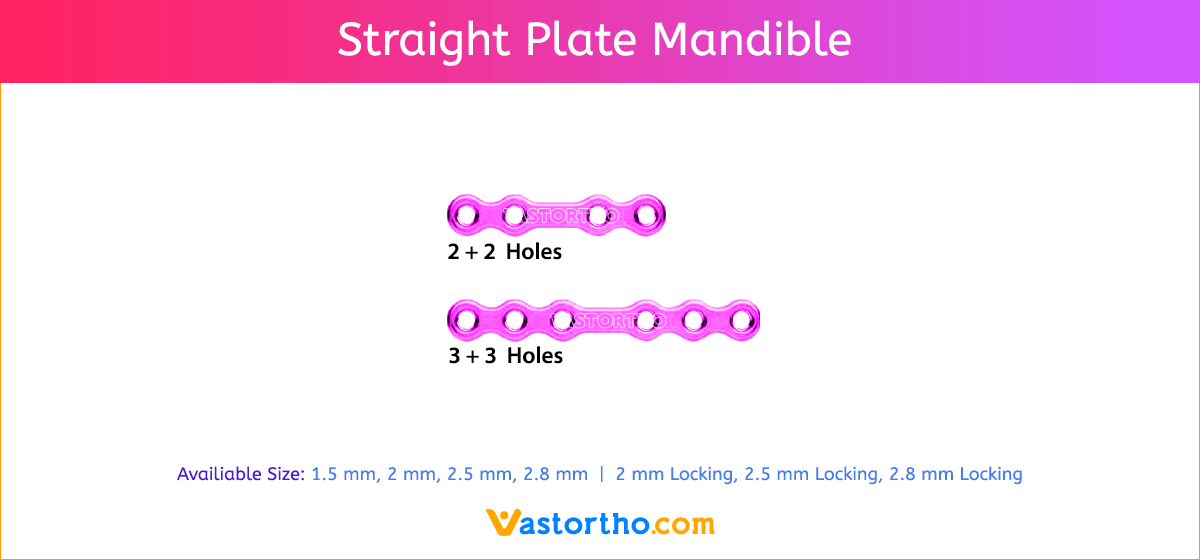
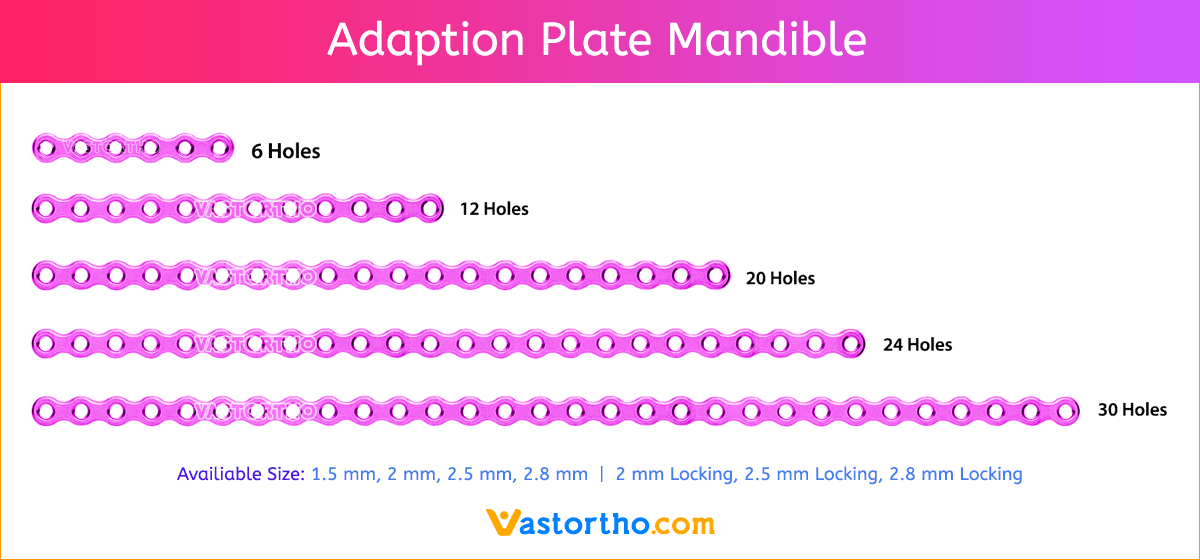
- Seven screw diameters to choose from: 1.5 mm, 2 mm, 2.5 mm, 2.8 mm, 2 mm Locking, 2.5 mm Locking and 2.8 mm Locking
- Rounded edges on plates for less irritation to soft tissue, where applicable
- Reduced plate/screw profile, where applicable
- Emergency screws available for each screw diameter
- Plates and Screws are made from pure Titanium
- Standardized instrumentation
- locking plate increases construct stability, decreases risk of screw back-out and subsequent loss of reduction. It also reduces the need for precise anatomic plate contouring and minimizes the risk of stripped screw holes.
Frame Plate Square Craniomaxillofacial Indications
Plate is intended for use in selective trauma of the midface and craniofacial skeleton, craniofacial surgery, reconstructive procedures, and selective orthognathic surgery of the maxilla and chin.