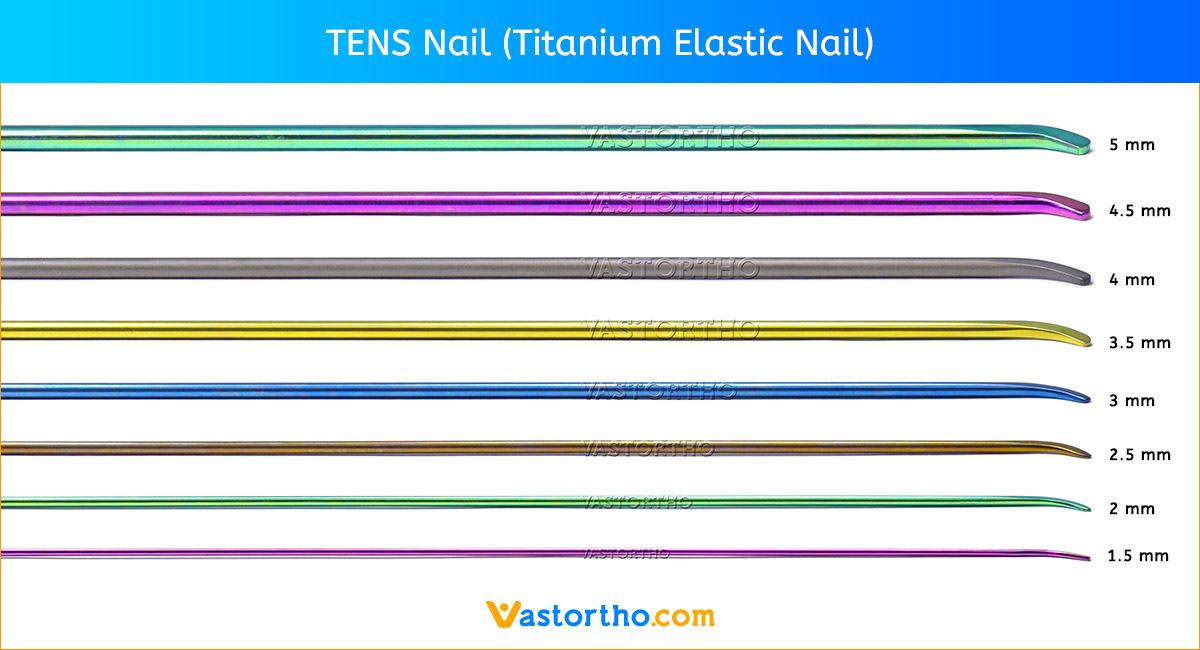
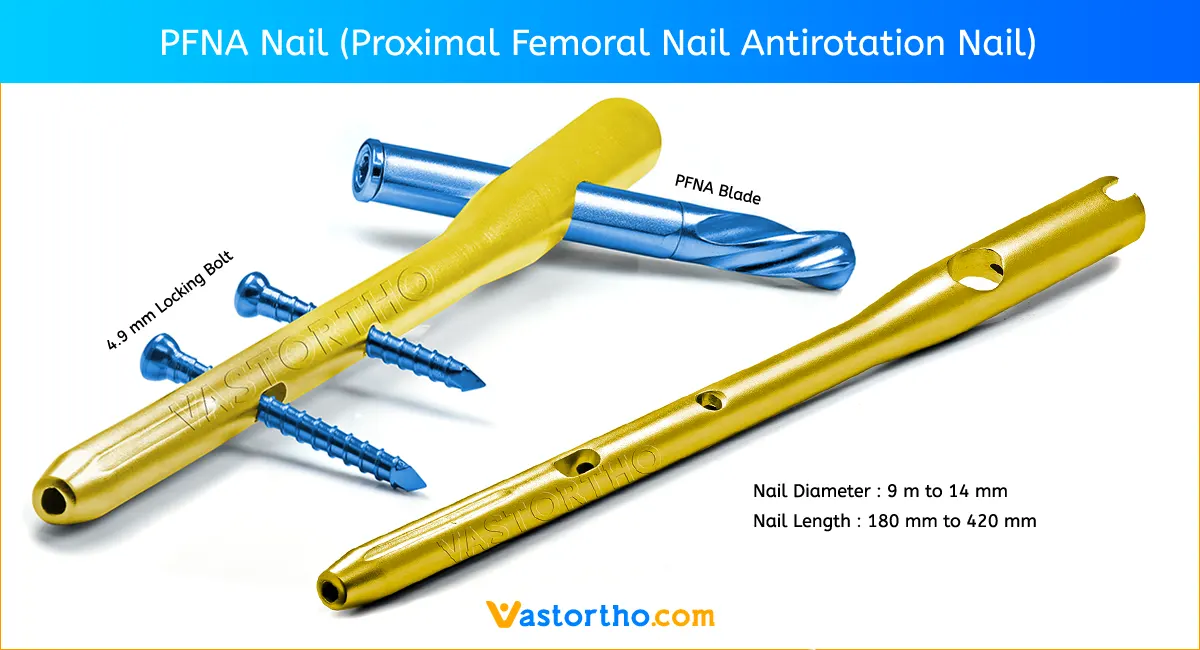
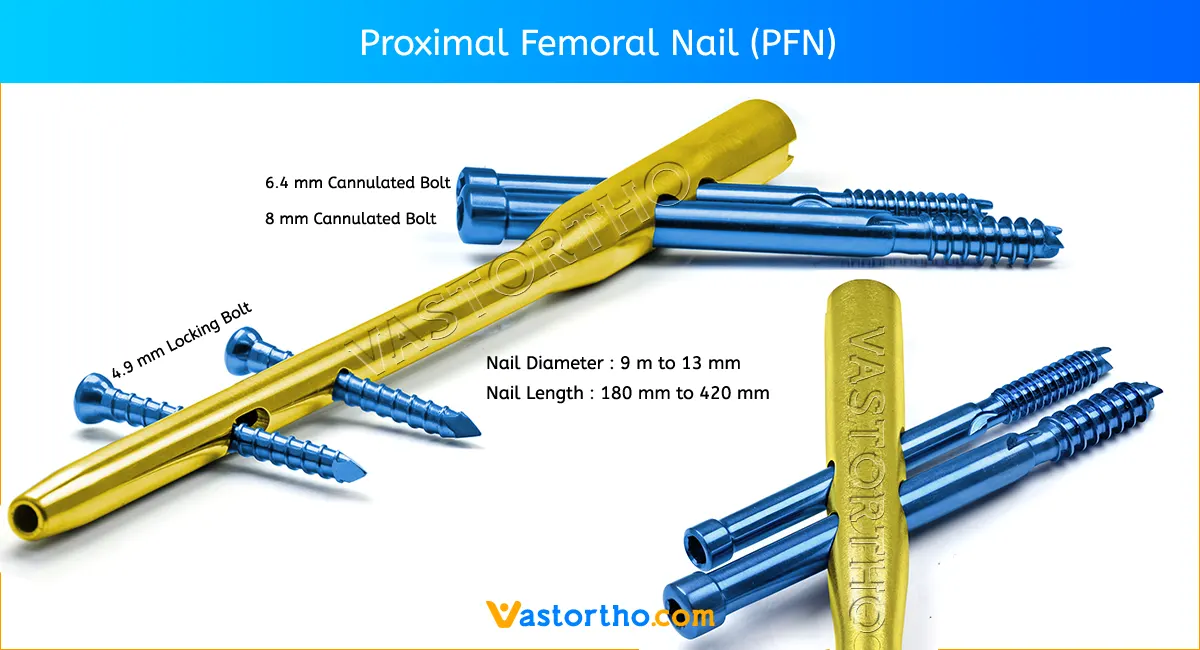
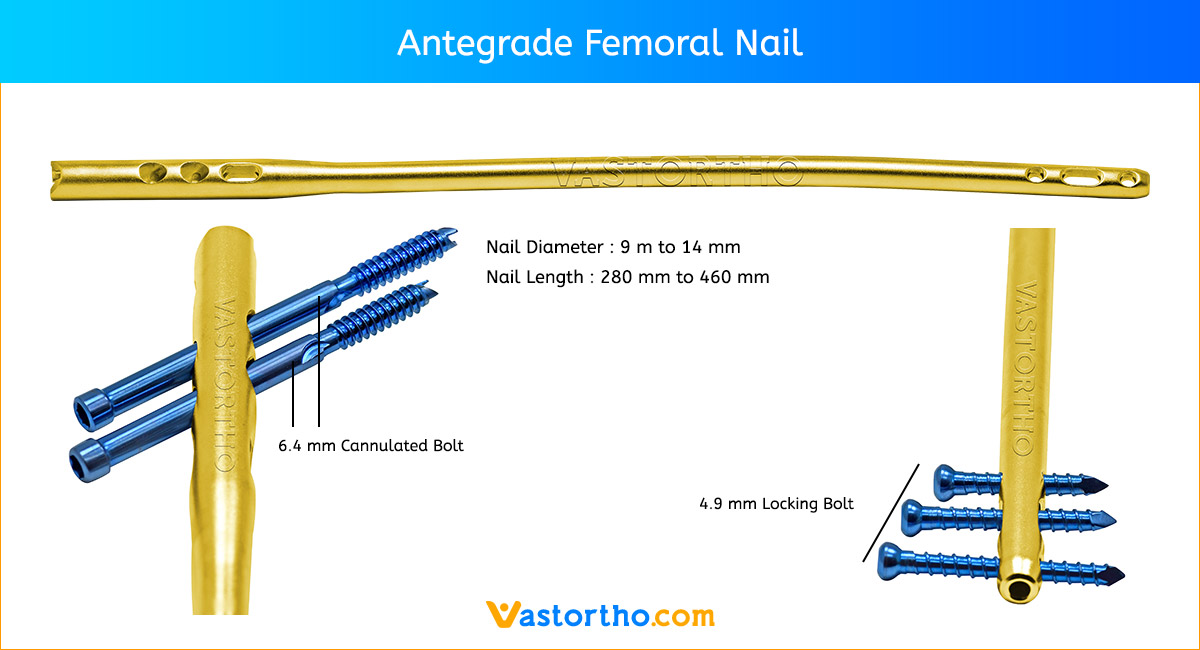
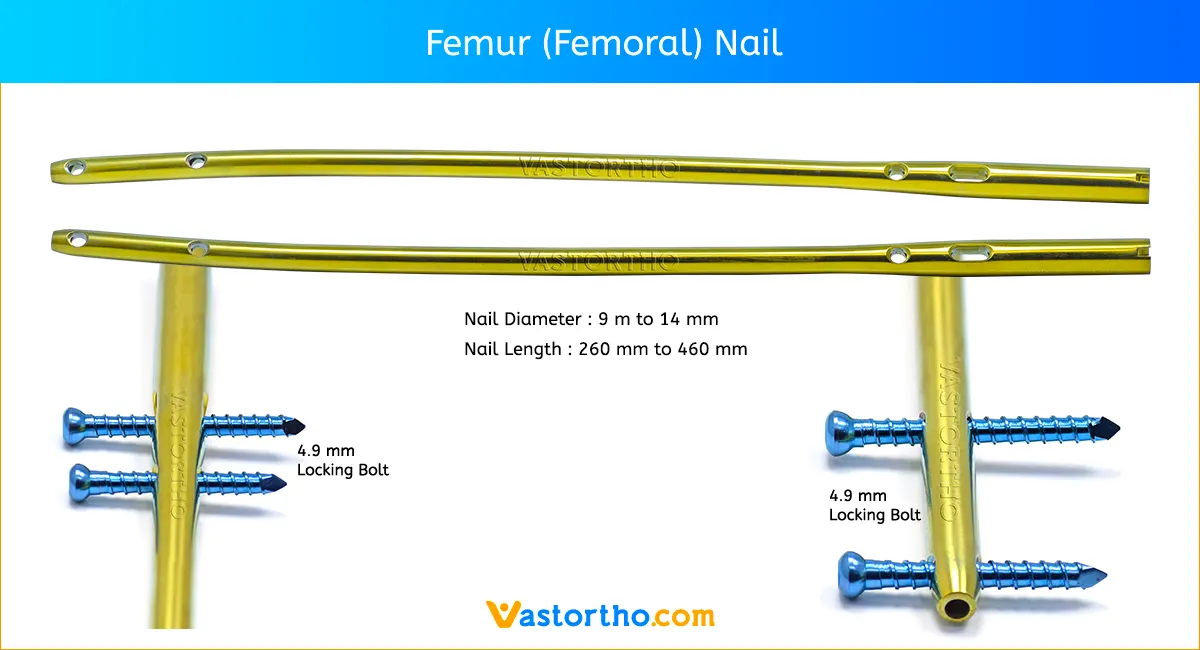
Inserting the TENS Nail (Titanium Elastic Nail)
Locate and maintain the entry hole with a fingertip while withdrawing the drill bit and introducing the nail. Using fluoroscopy, align the TENS Nail (Titanium Elastic Nail) tip so the convex side will glance off the far cortex. Advance the nail through the drilled entry hole by hand as far as possible.
Attach the Inserter with Universal Chuck onto the nail with a length of about 150 mm of nail between the inserter and entry point. The
longer this distance, the more difficult hammering will be since the nail will dampen the impact force. Tighten the inserter using the Spanner
Wrench.
Attach the Slide Hammer to the shaft of the inserter. Use controlled blows to drive the nail up the medullary canal.
Alternatively, the Hammer Guide and Inserter can be used for nail insertion. The alternative instruments are used in the same manner described for the Inserter with Universal Chuck.
Monitor nail advancement with fluoroscopy. Ensure that the convex side of the nail tip is glancing off the far cortex and is advancing with each blow. The nail will bend as it progresses up the canal. This part of the procedure requires the greatest insertion force.
Reducing the Fracture
Use the Small F-Tool to provide reduction forces on either side of the fracture gap To assemble the tool:
1. Thread one Threaded Rod at the end of the Bar.
2. Thread the second rod into the bar so the rods just fit across the leg.
3. Thread the third rod into the opposite end of the bar.
The Small F-Tool is placed on the leg at the level of the fracture so that both rods provide force on the opposing fragments to aid reduction.
Drive the first TENS Nail (Titanium Elastic Nail) to the level of the fracture. In a similar manner to that previously described, open the femur on the opposite side and insert the second TENS Nail (Titanium Elastic Nail) up to the level of the fracture.
Crossing the fracture
Visualize the fracture with fluoroscopy. Determine which TENS Nail will be easier to pass across the fracture. Advance that nail which will most effectively pull the proximal fragment into alignment. Using the Inserter with Universal Chuck and Detachable Slide Hammer, drive the nail
across the fracture, monitoring nail position with fluoroscopy. Alternatively, the Hammer Guide and Inserter may be used with the Detachable Slide Hammer to drive the nail.
The Titanium Elastic Nail can be rotated to manipulate the curved tip across the fracture. Rotation is easiest while the nail is being advanced or retracted.
Care should be taken not to twist the nails more than 90°. Otherwise, a “corkscrew phenomenon” may be created and stability will be lost. Rotating the nail while it is stationary may loosen the Inserter.
Advance the nail into the proximal fragment only enough to ensure reduction will be maintained. Further advancement may cause displacement of
the proximal fragment making it more difficult to pass the second nail. Confirm nail position in both the AP and lateral views.
Using the Inserter and Slide Hammer, drive the second nail across the fracture and into the proximal fragment. Continue advancing this nail until it is just distal to the proximal physis. Advance the other nail to the same level. The two nails should diverge in opposite directions, both medial and lateral, for optimal rotational stability. If the fracture is distracted, release traction and impact the
patient’s heel.
Cutting the TENS Nail (Titanium Elastic Nail) to length
Prior to cutting the TENS Nail to length, verify the position of the nails in relation to the rotation of the leg. Once the nail is inserted to its final position, mark the nail with a pen or clamp at the planned cutoff point. (The cutoff point should be 10 –20 mm outside of the cortex.)
Retract the nail far enough to access the cutoff point from outside the incision (usually 25–50 mm).
Bend the Titanium Elastic Nail end away from the bone to deform it slightly (approximately 10–15° of permanent deflection). This will allow the protruding nail end to sit slightly off the cortex for easy removal while remaining low-profile to minimize soft tissue irritation.
Cut the nail with the Rod Cutter to the appropriate length. Reinsert the nail with either the Standard Tamp or Beveled Tamp and Hammer. The Standard Tamp captures 2 mm of nail tip.
The Beveled Tamp captures 6 mm of nail tip and will leave approximately 10 mm of nail protruding from the cortex when the tamp is driven flush to the periosteum. Keep the etched line aligned with the long axis of the bone to keep the beveled surface in proper orientation. In order to prevent distraction of the fracture, a slight blow on the knee is recommended.
Confirm final nail position and fracture reduction with fluoroscopy. In its final position, the end of the nail should protrude 10–20 mm
outside the cortex at an angle approximately 10–15° above the bone. If the nail has been overinserted, use the Locking Pliers to grip and retract the nail.