4.5/5 mm Locking T Plate Specification, Uses, Sizes & Surgical Instruments.
4.5/5 mm Locking T Plate Design
Fixed angle stability:
The threads on the head of the locking screws lock into the threaded plate holes to form a fixed-angle construct that will increase load transfer between the plate and bone. When compared to conventional plate-and-screw constructs, the angular and axial stability of locking screws increases the strength of the construct under load without requiring precise anatomical contouring.
4.5/5 mm Locking T Plate Specification
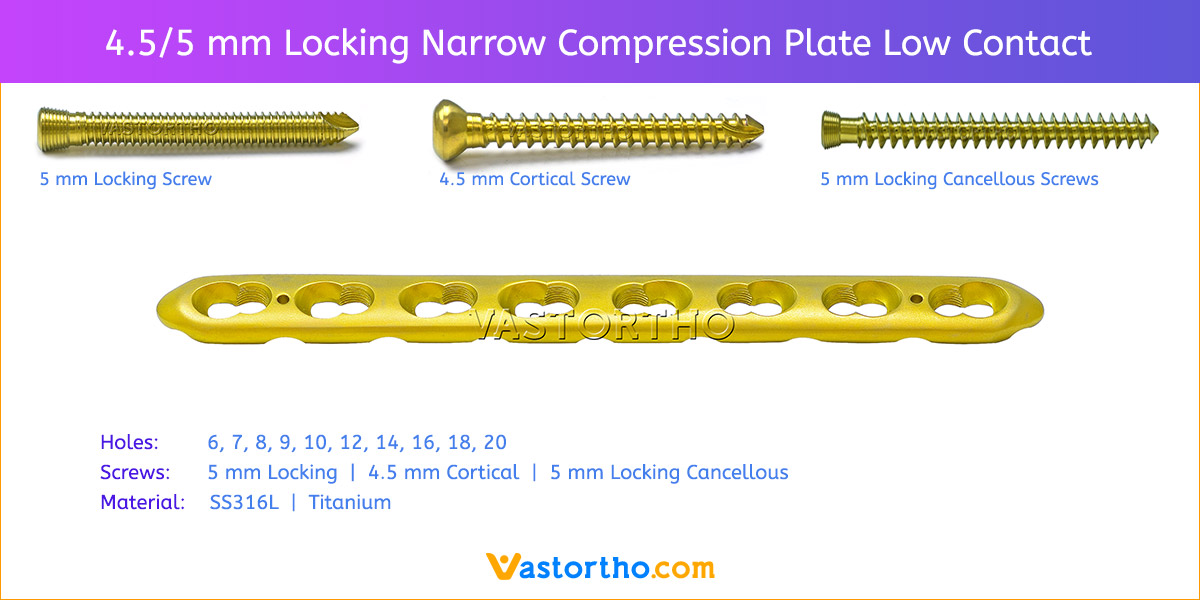
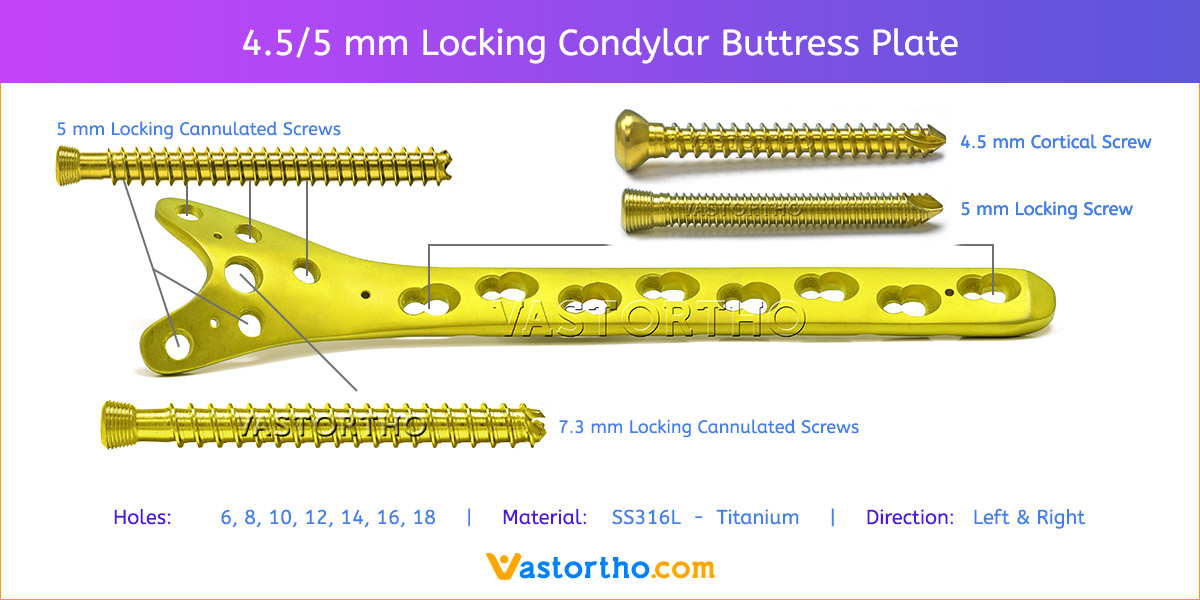
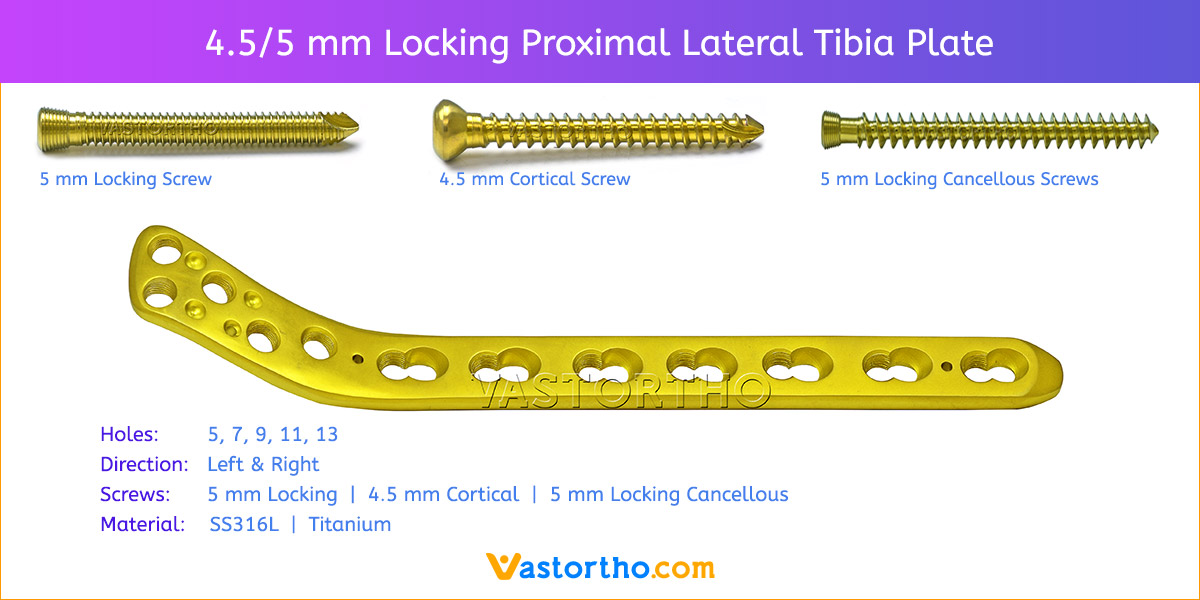
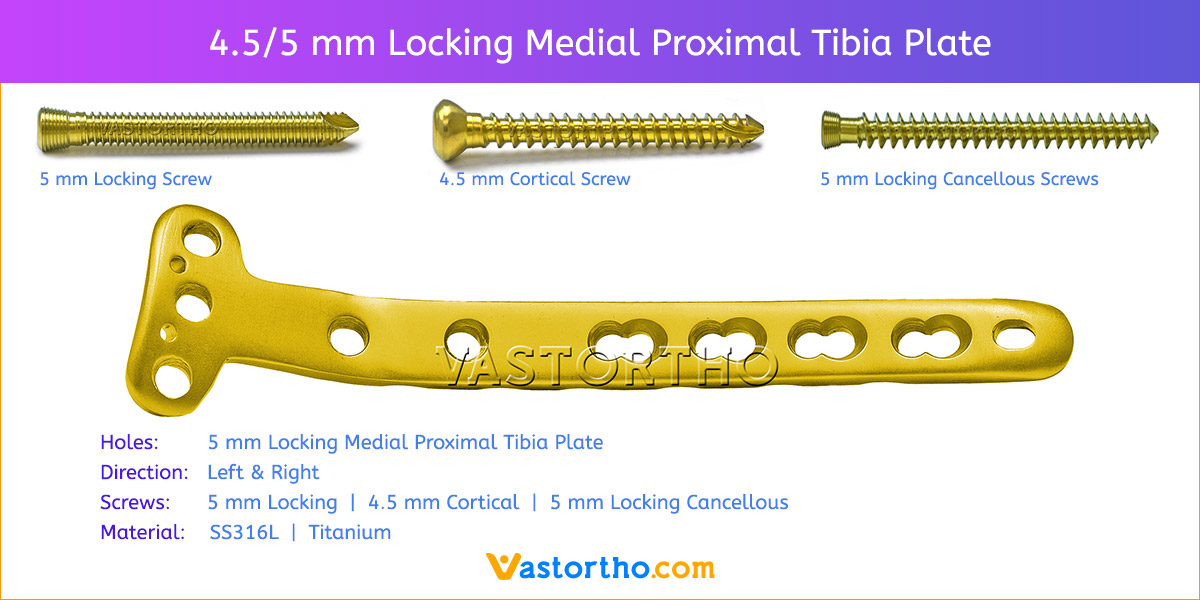
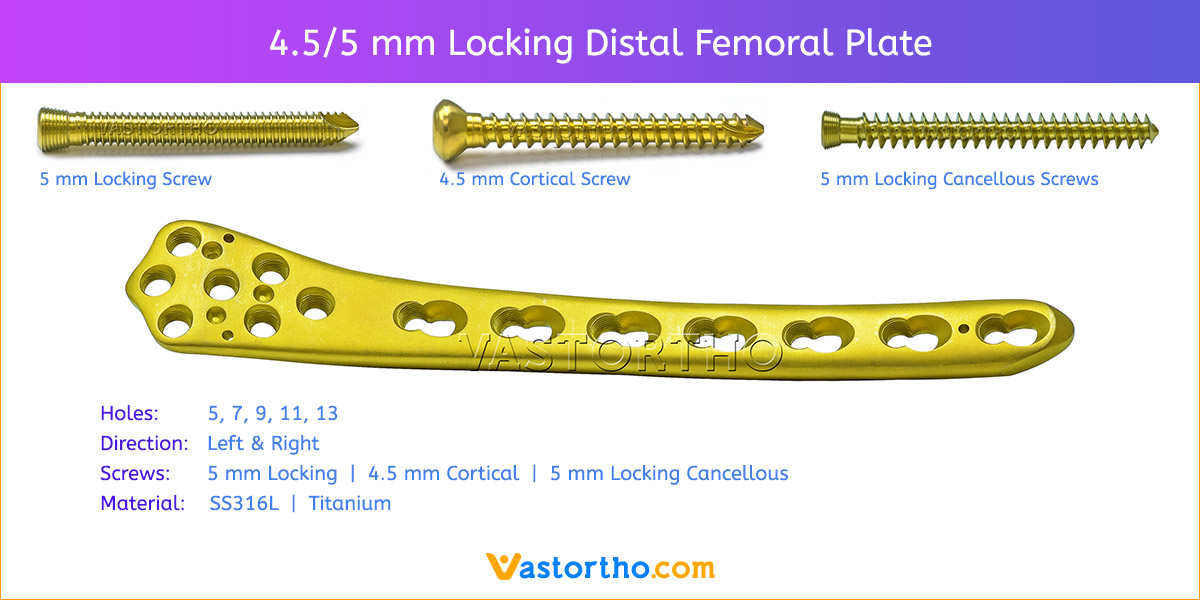
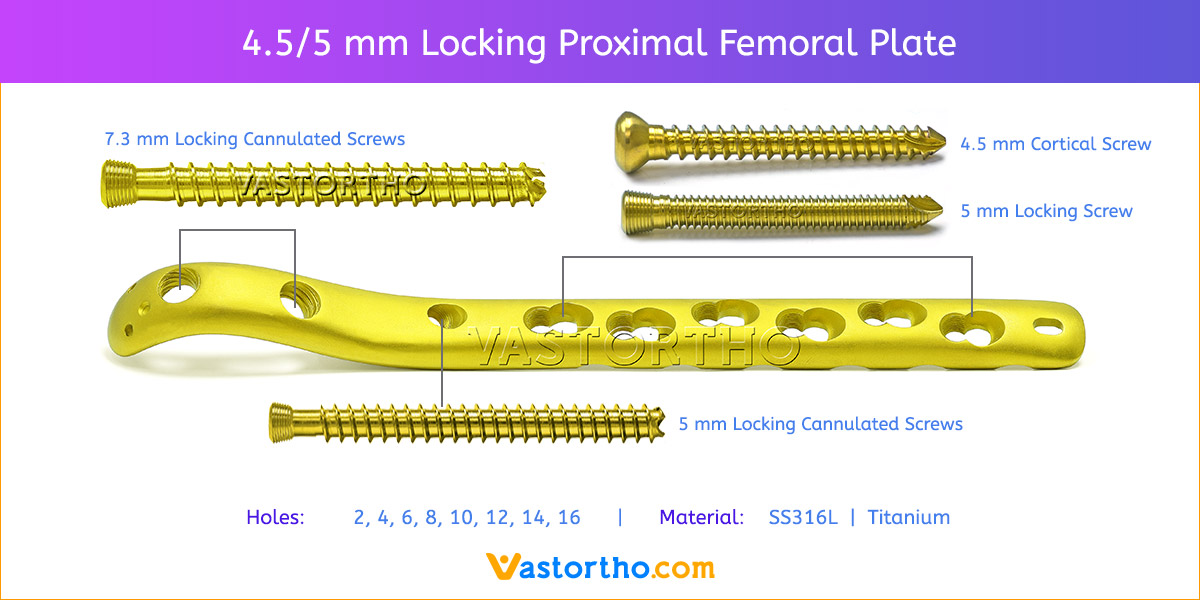
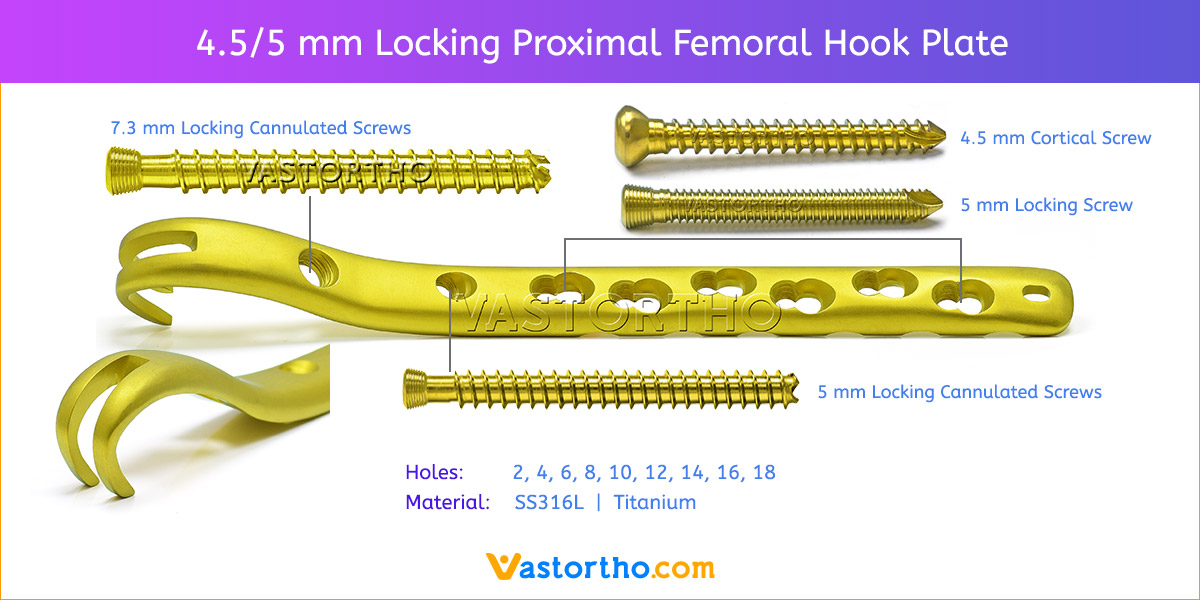
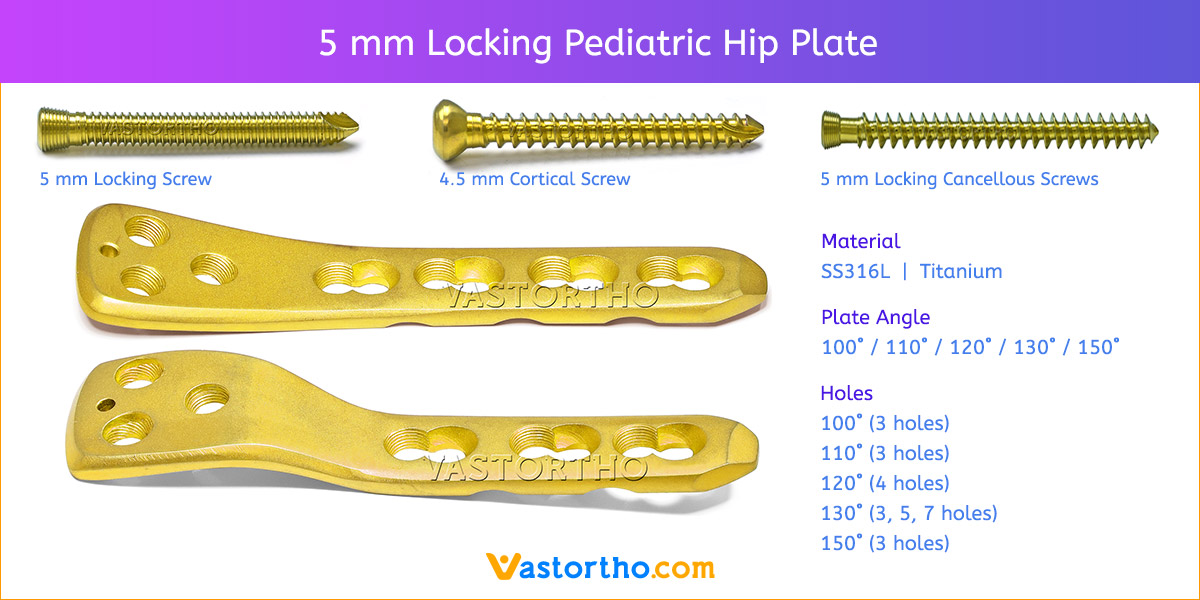
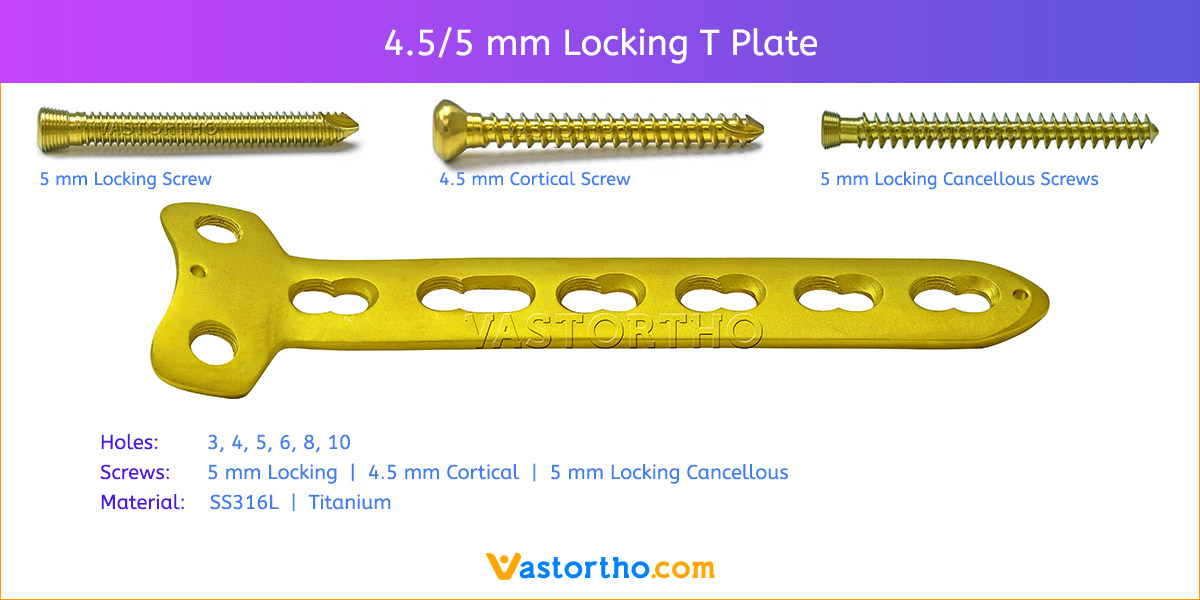
- Plates available holes are 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 10.
- Plate has combi holes and round holes. Combi holes allow fixation with locking screws in the threaded section and cortex screws in the dynamic compression unit section for compression.
- The shaft holes accept 5 mm locking screws in the threaded portion or 4.5 mm cortical screws or 5 mm Locking cancellous screws in the compression portion. Distal locking holes in plate head accept 5 mm locking screws or 4.5 mm cortical screws.
- 4.5/5 mm Locking T Plate allow implant placement to address the individual fracture pattern.
- Choice of different lengths of plate eliminates the need to cut plates.
- Pre-contoured plate to match anatomical shape.
- Available in both Titanium and Stainless steel.
- locking plate increases construct stability, decreases risk of screw back-out and subsequent loss of reduction. It also reduces the need for precise anatomic plate contouring and minimizes the risk of stripped screw holes.
- A complete Instruments Set is available for 4.5/5 mm Locking T Plate. General Instruments are available for this plate such as Plate Bending Press, Plate Holding Forceps, Plate Bending Pliers, Bone Holding Forceps, Bone Elevators, Bone Cutter, Bone Nibbler, Depth Gauge, Sleeve, Screw Driver, Trocar Sleeve etc.
4.5/5 mm Locking T Plate Uses
4.5/5 mm Locking T Plate is indicated for fixation of fractures, osteotomies and non-unions of the clavicle, scapula, olecranon, humerus, radius, ulna, pelvis, distal tibia, fibula, particularly in osteopenic bones.