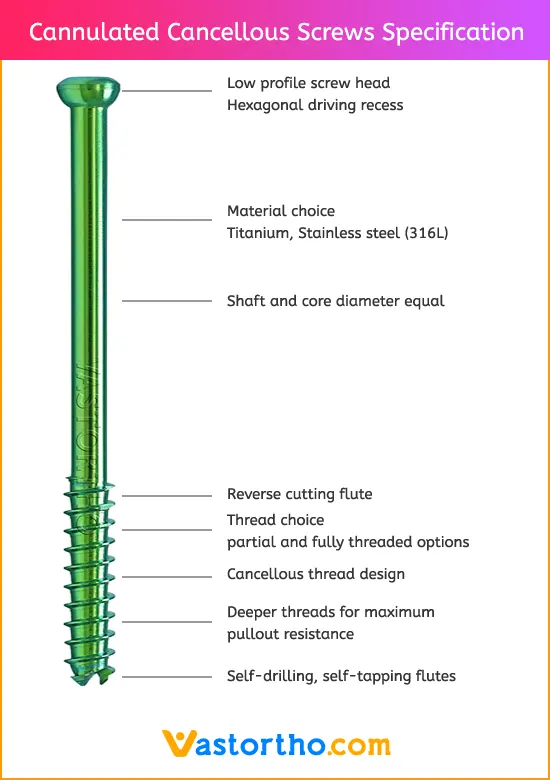
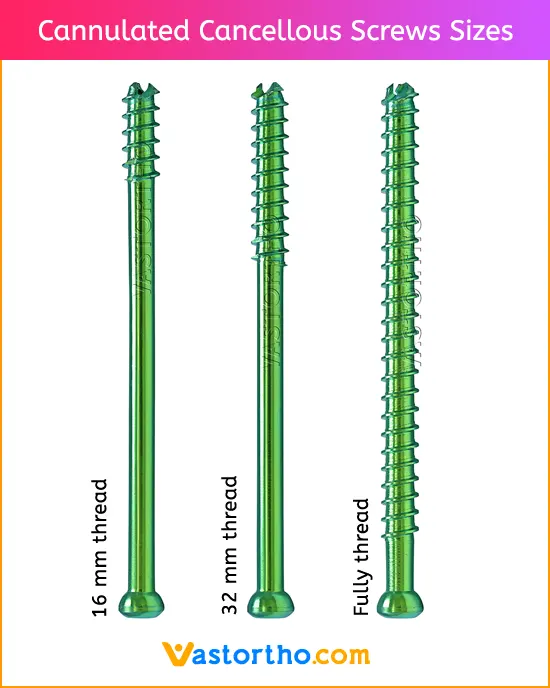
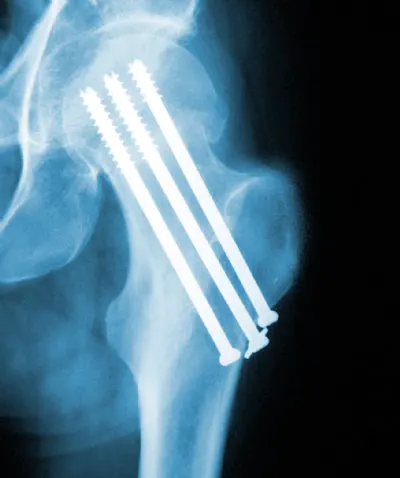
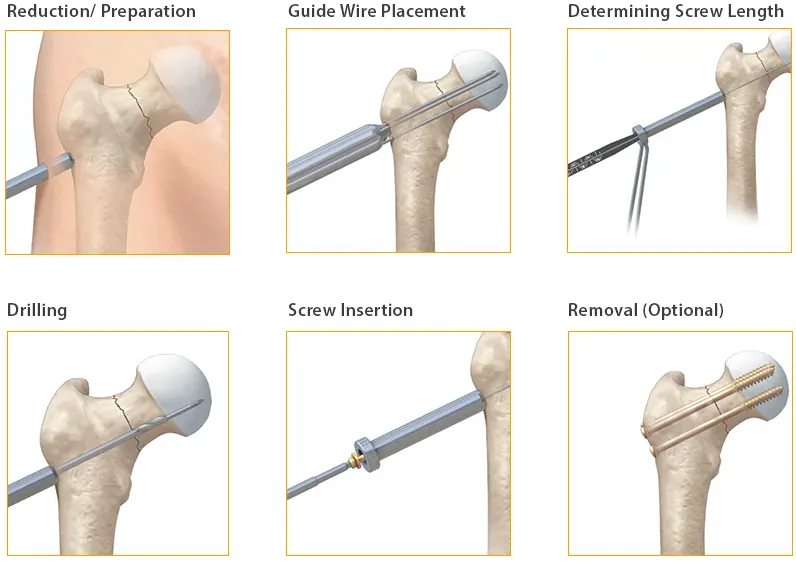
Cannulated Cancellous Screws General Adverse Events
As with all major surgical procedures, risks, side effects and adverse events can occur. While many possible reactions may occur, some of the most common include: Problems resulting from anesthesia and patient positioning (e.g. nausea, vomiting, dental injuries, neurological impairments, etc.), thrombosis, embolism, infection, nerve and/or tooth root damage or injury of other critical structures including blood vessels, excessive bleeding, damage to soft tissues incl. swelling, abnormal scar formation, functional impairment of the musculoskeletal system, pain, discomfort or abnormal sensation due to the presence of the device, allergy or hypersensitivity reactions, side effects associated with hardware prominence, loosening, bending, or breakage of the device, mal-union, non-union or delayed union which may lead to breakage of the Cannulated Cancellous Screws, reoperation.
 https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/4.5-mm-Cannulated-Cancellous-Screws.webp
550
1200
VastOrtho
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/Vast-Ortho-Logo-for-website.png
VastOrtho2023-06-17 21:22:222023-07-22 12:20:054.5 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screw
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/4.5-mm-Cannulated-Cancellous-Screws.webp
550
1200
VastOrtho
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/Vast-Ortho-Logo-for-website.png
VastOrtho2023-06-17 21:22:222023-07-22 12:20:054.5 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screw https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/5-mm-Locking-Cannulated-Cancellous-Screws.webp
550
1200
VastOrtho
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/Vast-Ortho-Logo-for-website.png
VastOrtho2023-06-17 21:14:492023-07-22 12:22:475 mm Locking Cannulated Cancellous Screw
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/5-mm-Locking-Cannulated-Cancellous-Screws.webp
550
1200
VastOrtho
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/Vast-Ortho-Logo-for-website.png
VastOrtho2023-06-17 21:14:492023-07-22 12:22:475 mm Locking Cannulated Cancellous Screw https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/6.5-mm-Cannulated-Cancellous-Screws.webp
550
1200
VastOrtho
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/Vast-Ortho-Logo-for-website.png
VastOrtho2023-06-17 20:28:382023-07-22 12:25:076.5 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screw
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/6.5-mm-Cannulated-Cancellous-Screws.webp
550
1200
VastOrtho
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/Vast-Ortho-Logo-for-website.png
VastOrtho2023-06-17 20:28:382023-07-22 12:25:076.5 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screw https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/7-mm-Cannulated-Cancellous-Screws.webp
550
1200
VastOrtho
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/Vast-Ortho-Logo-for-website.png
VastOrtho2023-06-17 20:19:352023-07-22 12:27:387 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screw
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/7-mm-Cannulated-Cancellous-Screws.webp
550
1200
VastOrtho
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/Vast-Ortho-Logo-for-website.png
VastOrtho2023-06-17 20:19:352023-07-22 12:27:387 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screw https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/7.3-mm-Cannulated-Cancellous-Screws.webp
550
1200
VastOrtho
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/Vast-Ortho-Logo-for-website.png
VastOrtho2023-06-17 20:05:042023-07-22 12:32:347.3 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screw
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/7.3-mm-Cannulated-Cancellous-Screws.webp
550
1200
VastOrtho
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/Vast-Ortho-Logo-for-website.png
VastOrtho2023-06-17 20:05:042023-07-22 12:32:347.3 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screw https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/7.3-mm-Locking-Cannulated-Cancellous-Screws.webp
550
1200
VastOrtho
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/Vast-Ortho-Logo-for-website.png
VastOrtho2017-11-28 05:29:512023-07-22 12:33:077.3 mm Locking Cannulated Cancellous Screw
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/7.3-mm-Locking-Cannulated-Cancellous-Screws.webp
550
1200
VastOrtho
https://www.vastortho.com/wp-content/uploads/Vast-Ortho-Logo-for-website.png
VastOrtho2017-11-28 05:29:512023-07-22 12:33:077.3 mm Locking Cannulated Cancellous Screw