Locking Trochanter Stabilizing Plate Specification, Uses, Sizes and Surgical Techniques

Locking Trochanter Stabilizing Plate Specification
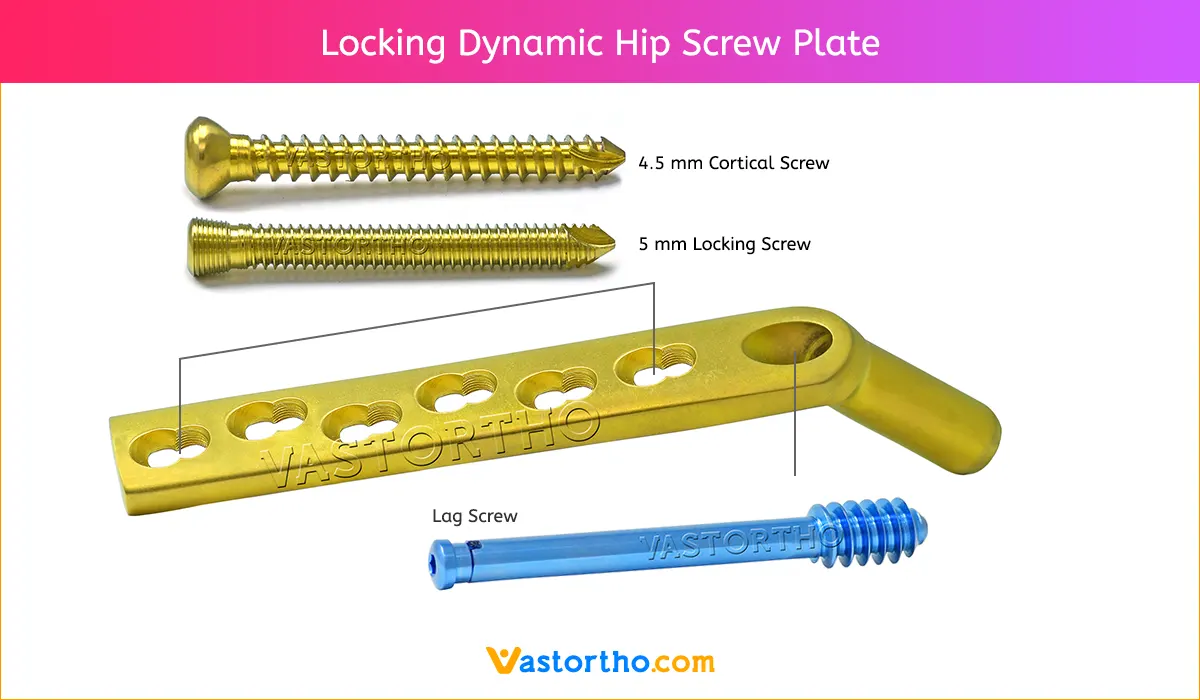
Locking Trochanter Stabilizing Plate has been designed as an extension to the Dynamic Hip Screw Plate and serves the following functions:
- It limits diaphyseal medialisation by fastening onto the greater trochanter.
- It enables the insertion of an additional cranial and parallel antirotation screw, which acts as a superolateral tension band. When used, the atirotation screw imposes a slightly more caudal positioning of the screw compared to the standard technique.
- It allows for an additional proximal internal fixation of the greater trochanter with locking head screws.
- It maintains the dynamization capacity of the Dynamic Hip Screw Plate.
Advantages of angular stability
Locked angle-stable screws can be fixed monocortically, even in soft bone without any risk of screw loosening. Due to the high stability of the screws in the plate, the greater trochanter can be secured as a functional entity without using cerclage wires. Fix the plate over or through the gluteus medius muscle without compressing the bone. As an internal fixator, the plate preserves bone vascularity.